America’s Great Salt Lake could be at risk of ecosystem collapse if it doesn’t get urgent and significant interventions.
The worst-case scenario is that rising salinity levels will impede ecological recovery at the world-famous saltwater body, according to findings presented by the Geological Society of America’s 2022 Connects Conference, Colorado, this past weekend.
More than a century ago, water from Utah’s huge lake was diverted for human consumption. A 2017 study EstimateEach year, approximately 3.3 trillion liters water is rerouted to the lake. This is mostly for agricultural purposes.
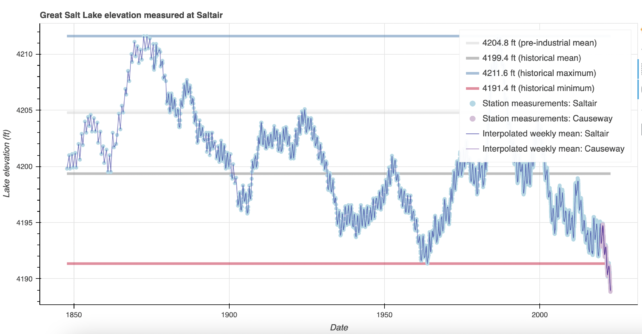
The state has fallen into a megadrought since then, further reducing fresh water intake to the lake and setting a new record in terms of lowest ever recorded water levels.
Early reports from this year suggest that the Great Salt Lake is already in existence Since the 1980s, it has shrunk by 2/3And The dramatic dropIt is exposing an ecosystem that all people, animals, and industry depend upon.
Joel Ferry, Executive Director of Utah Department of Natural Resources, said that “This is not a record we would like to break.” This was earlier in the year.
“Urgent action must be taken to protect and preserve this precious resource. The lake is in dire need of help.
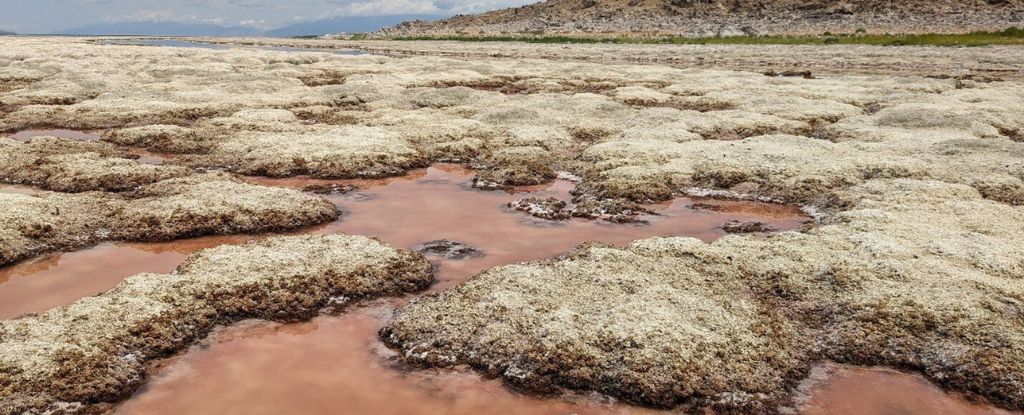
Utah’s lake One of the very few places on EarthWhere mineralized underwater reefs, known as microbialites, still grow.
These structures look like rocks but contain dense concentrations algae and bacteria. In fossil form, They are also known as stromatolitesThey are the oldest known evidence of life on Earth.
As the Great Salt Lake continues to sink, modern versions are slowly drying out. They turn from dark green and white as the water meets the microbial mats. The remains of bleached coral appear to be recovering Only When it is returned to water with a suitable salt.
The problem is that the Great Salt Lake is shrinking and becoming more concentrated with salt. In 2022, researchers anticipate that the Great Salt Lake will be a concentrated salt lake. MeasuredSome spots have salinity levels up to 26 percent. This is a significant difference from the more common lake salinity of about 15 percent.
Carie Frantz, a biologist at Weber State University, says that microbial mat recovery can be very slow and weak under these extreme conditions.
Frantz has been leading a group of undergraduate students over several summers to monitor the lake’s microbioites in the field as well as the lab to determine what happens to bleached coral reefs when they are re-submerged.
“Last Year, it was really encouraging, as we saw they can come back, fast,” she stated. explains.
“We saw something quite different this year, we don’t see the clear increase that we saw last year. These salinity levels are too high for organisms. It’s possible they don’t have the right conditions to grow.
This trend is very similar in nature to the one that occurred in the Great Salt Lake’s northern portion after the construction of a causeway back in the 1950s. The lake-crossing railroad divided the water body into two parts.
The southern section is the most dependent on fresh water and the northern portion became dangerously salty.
A mass death of photosynthetic microbes took place in the lake when salinity was 25 percent. This caused a pinkish hue. Space can be seen.
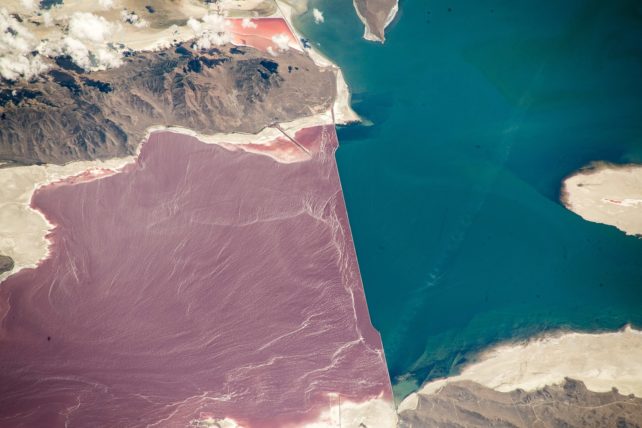

Only some microbes are able to survive in this environment. The Great Salt Lake is ten times saltier than ocean water. They are the ones that can survive in the Great Salt Lake. They turn sunlight into nutrients that will feed the brine shrimps, brine flies, then eventually the waterbirds.
Dust and Mercury pollutionIf the lake continues drying out, it could be an issue in the future. California residents experienced the same fate when a lake they shared was destroyed. Many more people have suffered from cardiovascular and asthma issues..
According to a Recent ReportFrom The New York TimesHigh levels of arsenic are also found in the lake’s bottom. These poisons could be carried to the lungs of those living near the shoreline if the shoreline recedes and exposes the lakebed to wind.
Salt Lake City legislators made efforts to conserve water, but researchers worry that these changes are not keeping up with the times. Climate Changeor rising water needs
Frantz and her colleagues’ findings are only optimistic if policymakers take decisive action.
“[If]The Great Salt Lake will rebound soon due to a combination of societal changes in water use, high precipitation years, and the microbialite community might be able recover,” said the team WritesThey are abstract.
Frantz worries that this will not happen. Frantz says this is an emergency and that the body of water is becoming ever more salty, making it harder for microbes to recover.
“We are not responding as quickly as the situation requires.” says FrantzA recent GSA press release.
Bonnie Baxter, a Westminster College biology professor, also shares this concern. She Telled The New York TimesIn June, the Great Salt Lake Ecosystem was on the brink of collapse.
“It’s terrifying.”


