People often fear the mere mention of radiation. Some people find it entertaining to think that radiation could transform them into super heroes. The Hulk.
Is it true that everything around us, including the food we eat, is radioactive? It is possible that you have heard bananas are radioactive. But what does it actually mean? Even though we are not superheroes, is human body radioactive as well?
What is radiation?
RadiationRadiation can be described as energy that travels through space in waves or as particles. Each day we are exposed radiation from many natural and artificial sources.
Natural radiation can be found in all forms: cosmic radiation from the Sun, outer space, radiation from soil and rocks, radioactivity in our food, water, and air.
Bananas can be used as a natural radiation source. These bananas are high in potassium, which is radioactive. But there’s no need to give up your banana smoothie – the amount of radiation is extremely small, and far less than the natural “background radiation“We are exposed every day.
Artificial sources of radiation can include medical treatments, Xrays, mobile phones, and power lines. The common belief is that artificial radiation sources are more dangerous than natural radiation. This is false.
Artificial radiation is not different from natural radiation in any way. The dose is the main factor in causing harmful effects.
What is the difference in radiation and radioactivity?
The words ““Radioactivity” and radiation” is often used interchangeably. Both words are sometimes used interchangeably.
Radioactivity is the process of an unstable atom going through radioactive decay. As the atom attempts to achieve stability or become non-radioactive, energy is released as radiation.
Radioactivity refers to the material’s decay rate and the process by which it does so. Radioactivity is the process of elements and materials trying to become stable. Radiation can be considered the energy released by this process.
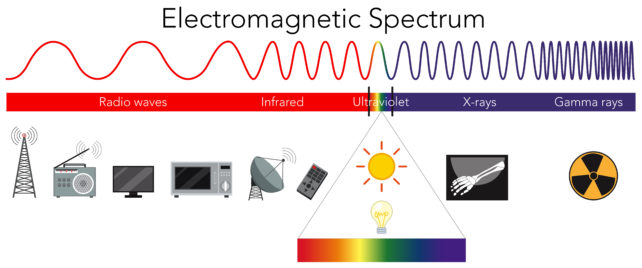
Ionizing as well as non-ionizing radiation
Radiation can be divided into two types depending on its energy level.
Ionizing radiationIt has enough energy to destroy an electron from anatom. This can alter the chemical composition of a substance. Examples of ionizing radio include Xrays and radon, a radioactive gas that is found in soil or rocks.
Non-ionizing radiationAlthough it has less energy, it can still excite molecules or atoms and cause them to vibrate more quickly. Non-ionizing radiation is most commonly found in mobile phones, powerlines, and ultraviolet (UV) rays from the Sun.
Are all radiations dangerous? It is not.
Radiation is not always dangerous – it depends on the type, the strength, and how long you are exposed to it.
In general, radiation with a higher energy level is more likely to cause harm. We know for example that excessive radiation can cause skin cancer. ionizing radiation – say, from naturally occurring radon gas – Can cause DNA and tissue damage in humans.
We also know that non-ionizingRadiation such as the UV rays of the Sun can be dangerous If the person is exposed sufficiently to high intensity levelsThis can lead to adverse health effects, such as burns. CancerBlindness or,
These dangers are easily avoided because they are well-known and understood. International NationalExpert bodies provide guidance to ensure radiation protection for the environment and people.
For ionizing radiation, this means keeping doses above the natural background radiation as low as reasonably achievable – for example, only using medical imaging on the part of the body required, keeping the dose low, and retaining copies of images to avoid repeat exams.
Non-ionizing radiation means avoiding exposure above Safety limits. Radiofrequency non-ionizing radiation is used in telecommunications equipment, for example. Must operate within these safety limitations.
We also know that UV radiation from Sunlight can cause skin cancer. protect against exposureWear sunscreen and wear clothing when the UV index is 3 or more.
Radiation in medicine
Radiation exposure has clear risks, but it is important to understand the potential benefits. Radiation in modern medicine is a common example.
Medical imagingUses ionizing radiation techniques such as CT scans or X-rays. Also, uses non-ionizing radiation such as ultrasound. Imaging by resonance ( MRI).
These medical imaging techniques enable doctors to see inside the body, which can lead to quicker and more accurate diagnoses. It can also be used to rule out serious illnesses.
Radiation can also help treat certain conditions – it can Kill cancerous tissueA tumor can be removed or treated with chemotherapy. can be used to lower pain.
Are our bodies radioactive as well? Our bodies, like all things around us, are radioactive. However, this is nothing to be concerned about.
Our bodies were built to handle small amounts of radiation – that’s why there is no danger from the amounts we are exposed to in our normal daily lives. You shouldn’t expect radiation to transform you into a superhero anytime soon. That is science fiction.![]()
Sarah LoughranDirector Radiation Research and Advice, (ARPANSA), and Adjunct Professor (UOW). University of Wollongong
This article was republished by The ConversationUnder a Creative Commons License Please read the Original article.


