Many children grow up staring at the night sky and dreaming of becoming stars. astronautsWho dares to go after their dreams? The Moon – and beyond.
To be eligible for this job, potential astronauts must go through a competitive selection process. NASA’s 2021 class astronauts The space agencyThe company said it had chosen just 10 candidates among more than 12,000 applicants.
These are the essential requirements NASAThe requirements include US citizenship and a master’s degree in a STEM area, such as engineering, biological science or computer science. The astronauts must be physically fit and capable of passing NASA’s challenging physical exams.
NASA has been announcing its first class in astronauts since 1959. More than 350 people have been made astronauts.In a 2020 blog post, Anne McClain,NASA astronaut, John McCormick, summarized the NASA’s requirements for future spacefarers as follows: “Be adaptable. Trustworthy. Tenacious. Detail-oriented.”
During the space race – the Cold War-era competition between the US and the Soviet Union to be the first to explore space – military men were first in line to become astronauts.
Today, 12 men have walked on Moon Moon. They are all white men. Still, NASA’s astronaut corpsThe variety of its offerings has increased, and it has been more diverse over time. long-awaited 2024 Artemis missionThe agency hopes to land the first female astronaut and person of color on Mars.
To become fully qualified astronauts, NASA’s astronaut candidate, also known as ASCANs after the selection process, completes a two year training course. NASA trains its astronauts in many environments to prove their worth, including hot deserts or large pools.
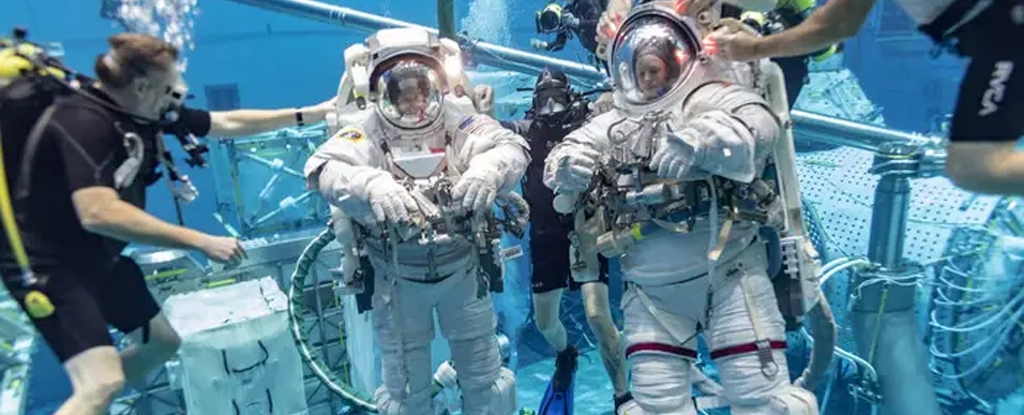
For astronauts who are preparing for trips outside the confines of spacecrafts, they train underwater in large indoor swimming pools. Swimming in pools simulates microgravity (or weightlessness) that astronauts will experience when they work in space.
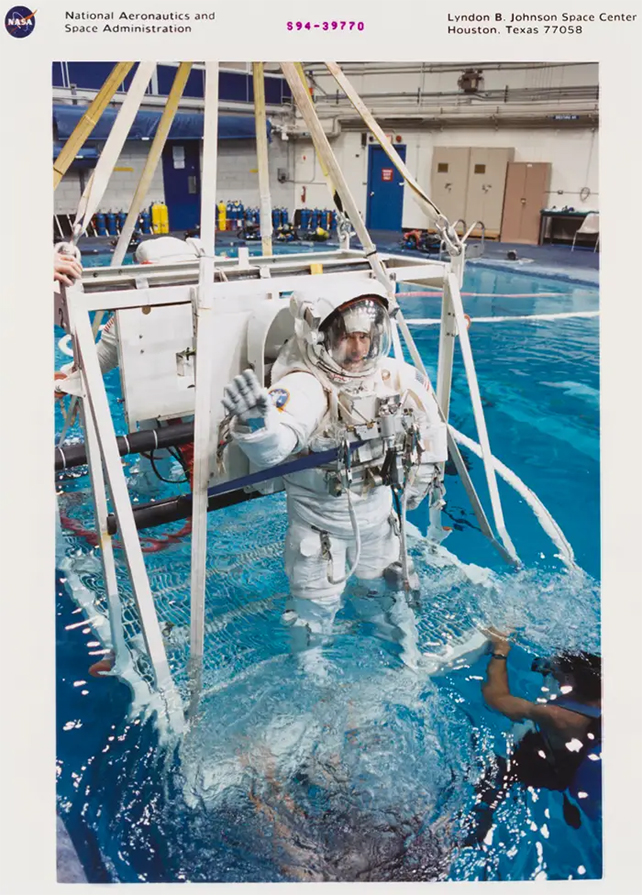

Using mock-ups of the spacecraft in the pool, astronauts practice spacewalks – when astronauts leave the spacecraft to work in the vacuum of space.
NASA conducts the most recent spacewalk training at Houston’s Johnson Space Center, Texas.
The massive pool – which contains 6.2 million gallons of water, according to NASA – has a partial mock-up of the International Space Station (ISS), so that astronauts can practice using hardware in a weightless environment.
NASA’s reduced gravity research program began in 1959 according to The Space agency. Astronauts can also take to the skies in zero gravity airplanes known as the “vomit camet,” which is part of this program.
According to the report, passengers will experience about 25 seconds of zero gravity after the plane reaches the top of the wave. NASA.
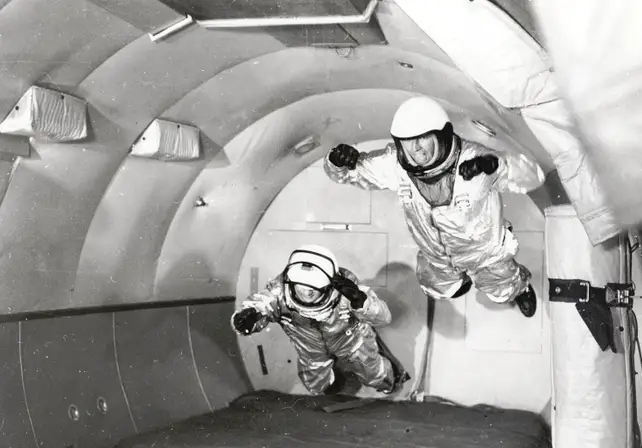

Over the years, several types of aircraft were involved in the program, including NASA’s KC-135A aircraft which was retired in 2004. According to NASA, Zero Gravity Corporation took over operations of zero gravity flights in 2008. The space agency.
The plane can also be used as a floating lab. Because of the plane’s rollercoaster-like maneuvers, researchers often perform medical experiments and motion sickness tests on these flights.
Sometimes, the plane was a Hollywood landmark. Zero gravity scenes were shot by Bill Paxton and Kevin Bacon. 1995’s “Apollo 13”Get aboard the Vomit Comet.
Since the Original Mercury 7 crewNASA astronauts learned survival skills in 1959 for if they had to land in an emergency in remote areas.
Apollo 11 astronauts went to Nevada in 1964 to practice survival skills and spend three days in the desert heat. They are wearing parachutes as parachutes to cool down in the desert heat.
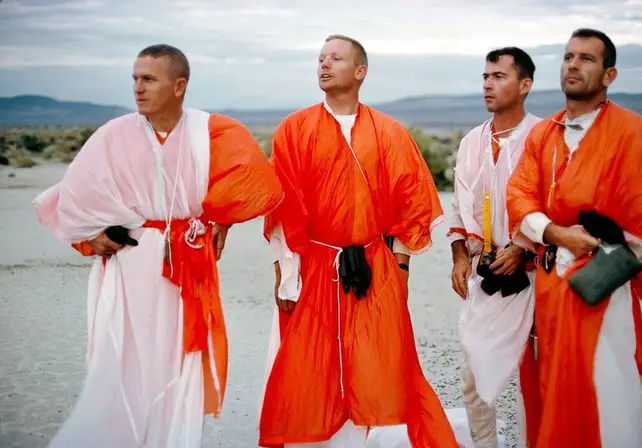

Because the desert environment is the most like an alien planet, NASA astronauts train there. Training for Artemis Moon rocket missions is part of the training. The space agency it will conduct two field trainings in the Arizona desert – which is similar to the Moon.
Astronauts were trained on a multiaxis trainer during the space race. This allowed them to spin at 30 revolutions per second. This contraption was called the “gimbal rig” and was intended to help astronauts get used to the disorienting ride they would experience while in a spacecraft tumbling through the air.
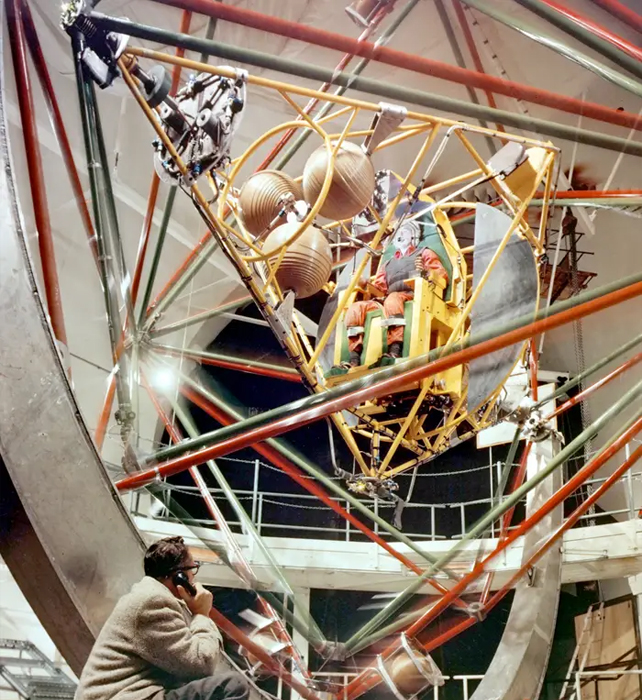

John Glenn, Project Mercury astronaut and NASA Glenn Research Center videographer, stated that “that was one of the most demanding tests or training exercises I went through anywhere on the entire training floor for spaceflight.” YouTube2016 2016
The rig was built in 1960 by seven of the original Project Mercury astronauts. Below, you can see the rig in action.
frameborder=”0″ allow=”accelerometer; autoplay; clipboard-write; encrypted-media; gyroscope; picture-in-picture” allowfullscreen>
NASA uses a different nameThis spinning contraption is used to train astronauts. Spacefarers are not required to control modern spacecraft’s spin.
NASA used a large machine known as a human centrifuge in the early days to assess gravitational stress for astronauts preparing to visit the Moon.
The human centrifuge features a rotating arm with a capsule capable of holding a human. Astronauts can test their tolerance for extreme gravitational force as the machine spins.
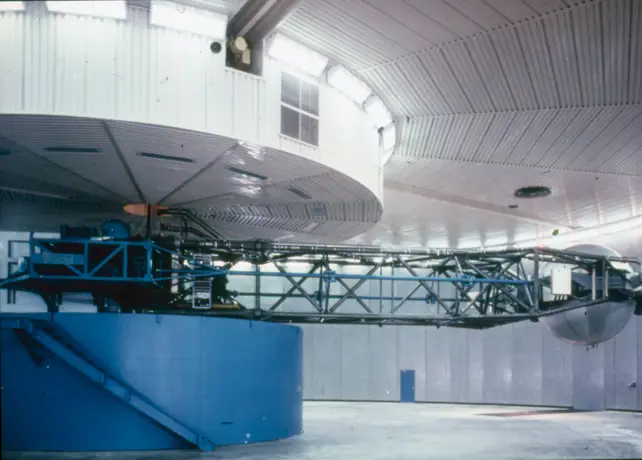

Glenn recalls, “Whirling around on the end of that long arms, I was acting like a guineapig for what a person might encounter when being launched into space/reentering the atmosphere,” Glenn said. 2000 memoir.
To screen potential astronauts, psychological and psychiatric screening is performed to determine if they are fit for space travel.
NASA started to recognize the mental strain of space travel as more people ventured into space.
“We had a payload specialist that was obsessed with the hatch. “All I have to do is turn the handle, and the hatch opens and all air goes out,” said Henry Hartsfield. It was scary,” Henry Hartsfield said in 1969 when he became a NASA astronaut. Interview from 2001An account of one of his early missions. “We began to lock it.”
It is extremely stressful to go into space. NASA released its 2016 human research program. ReportCrew members were exposed to radiation, sleep changes, gravity shifts, long periods of isolation, and radiation.
Crew members who have become astronauts regularly speak with medical staff (including psychologists) on board the ISS. private video conferences.
Considering NASA’s ambitious goals to send humans even farther into space – to the Moon and Mars – in the not-so-distant future, maintaining astronauts’ mental well-being will be an enduring challenge.
This article was first published in Business Insider.
Business Insider offers more information:


