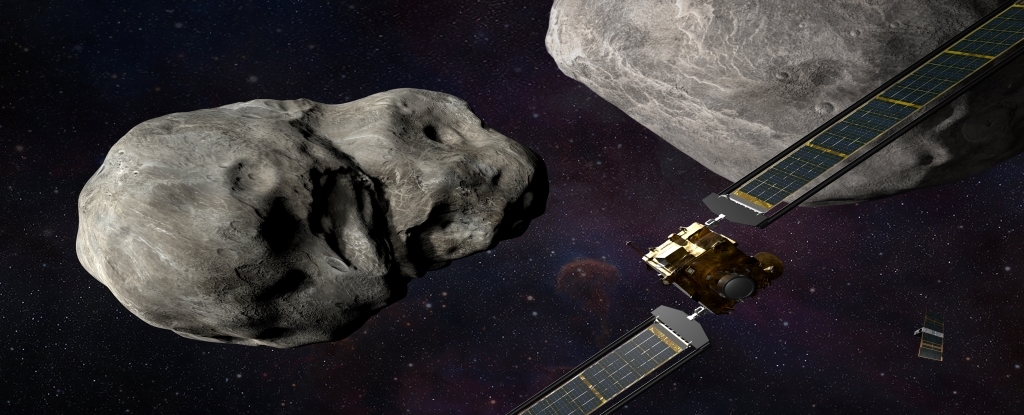
NASA’s DART Mission (Astronautics and Remote Sensing) will launch on September 26th at 11.15 UTC.Double Asteroid Redirection Test) will be the first to deliberately and measurably change the motion of a significant body in our Solar System.
It will also smash into an asteroid.
The mission will provide the first test of a technique that could be used in the future – to redirect any asteroids we detect on a collision course with Earth.
Below is a livestream:
frameborder=”0″ allow=”accelerometer; autoplay; clipboard-write; encrypted-media; gyroscope; picture-in-picture” allowfullscreen>
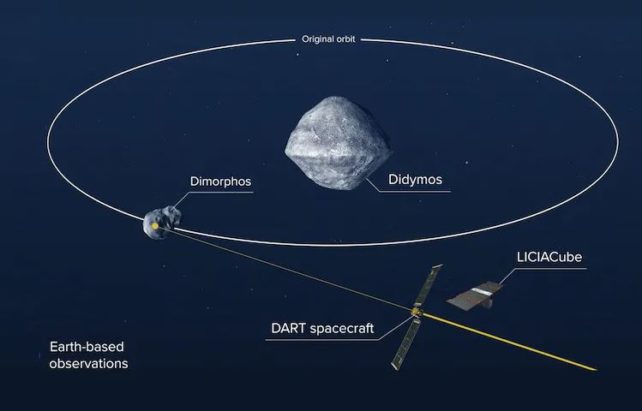
Binary pair of space rocks
DART was createdOn 24 November 2021, it reached its destination, a pair of asteroids orbiting each other around 11 million kilometers (6.84 million miles) away from Earth.
The larger of the two asteroid pairs is called DidymosIts diameter is 780m (just over half a mile). The smaller asteroid, measuring just 160 meters in width, is called Dimorphos. They orbit each other at a distance close to 1.18 km, and one orbit takes approximately 12 hours.
These asteroids pose no threat to Earth and were chosen partly as DART targets. Importantly, the asteroids are a binary pair which makes it possible for astronomers to evaluate the impact’s effects.
The sunlight reflected from asteroids increases and decreases as they orbit one another. Variables systematically during the orbit’s 12 hour cycle.
Astronomers can observe this variation using powerful telescopes on Earth.
The mission is difficult, but the physics is easy.
It sounds very simple and it is. To change the motion of one thing, you can combine it with another.. The execution of the mission can be very difficult.
After a 10-month journey, DART will reach the asteroids at 11 million kilometers. The spacecraft must use autonomous targeting. Images of asteroidsIt takes as it approaches.
DART must be able to identify the asteroids automatically, lock onto Dimorphos and adjust its trajectory in order to hit it. All this while traveling at nearly 24,000 km (close to 15,000 mi) an hour.
While the impact is easy to measure, it can be hard to predict its results. The impact will depend on the Dimorphos’ size, shape, composition, and exact location of DART.
All of these factors are uncertain. Completing computer simulations of the impacts have been done. The DART mission will focus on the comparisons between the predictions and measured results.
In addition to the measurements made by telescopes on Earth, it will also be possible from the Italian Space Agency to get a closer view of the impact. CubeSat(small type of satellite) LICIACubeThat was it A spring-loaded container is used for deploymentThe craft was aboard on September 11. LICIACube will be following the collision and taking photographs of its aftermath.

These results will reveal a lot about asteroids’ nature and our ability change their motions. This information could be used to plan for the future. Planetary defenseMissions to redirect asteroids that are deemed to pose a threat to Earth.
What is the level and nature of the threat?
If an asteroid is less than 25m (82 feet) in size, it could cause injury from an explosion. There are approximately 5 million of such objects in the Solar System. We have only discovered 0.4 percent.
This type of hit occurs about once in 100 years. While it can be quite common, the risk overall and the impact risk are very low.
There are 25,000 objects in our Solar System that are the size of Dimorphos. This means that Earth is likely to be hit every 20,000 year. A large object like this would result in mass casualties if they hit a densely populated area.

Asteroids which could pose a threat to human civilization exist in the one-kilometer plus category. These objects are less common than a thousand and may strike Earth once in 500,000 years. We have already found 95% of these objects.
Potential asteroid collisions can occur with Earth in a variety of ways. They could be benign and common, or they could be catastrophic and rare. DART tests for asteroids are being conducted at a relevant and interesting size: those over 100 meters.
DART’s success may open the door to future missions to target asteroids in order not to be in danger of collisions with Earth.
Asteroid collisions with Earth can be difficult. We need to give it a gentle push.
The “Bed of many” premise will be reaffirmed in the near future.Asteroid is on its way, so we must deflect it!” Movies could very well be a reality.![]()
Steven TingayJohn Curtin Distinguished Professor in Radio Astronomy Curtin University.
This article was republished by The ConversationUnder a Creative Commons License Please read the Original article.


